mirror of
https://github.com/revarbat/BOSL2.git
synced 2025-08-13 06:34:21 +02:00
doc reorganizing, minor bugfixes
This commit is contained in:
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// This file provides modules and functions to create a [VNF](vnf.scad) using metaballs, or from
|
||||
// general isosurfaces. Also provided are modules and functions to create [regions](regions.scad)
|
||||
// (lists of polygon paths) for 2D metaballs and 2D contours are also supported.
|
||||
// (lists of polygon paths) for 2D metaballs and 2D contours.
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// The point list in the generated VNF structure contains many duplicated points. This is normally not a
|
||||
// problem for rendering the shape, but machine roundoff differences may result in Manifold issuing
|
||||
@@ -1046,11 +1046,11 @@ _MSquareSegmentTable = [ // marching square segment table (lower res)
|
||||
/// _mctrindex() - private function
|
||||
/// Return the index ID of a pixel depending on the field strength at each vertex exceeding isoval.
|
||||
function _mctrindex(f, isoval) =
|
||||
(f[0] > isoval ? 1 : 0) +
|
||||
(f[1] > isoval ? 2 : 0) +
|
||||
(f[2] > isoval ? 4 : 0) +
|
||||
(f[3] > isoval ? 8 : 0) +
|
||||
(is_def(f[4]) && f[4] > isoval ? 16 : 0);
|
||||
(f[0] >= isoval ? 1 : 0) +
|
||||
(f[1] >= isoval ? 2 : 0) +
|
||||
(f[2] >= isoval ? 4 : 0) +
|
||||
(f[3] >= isoval ? 8 : 0) +
|
||||
(is_def(f[4]) && f[4] >= isoval ? 16 : 0);
|
||||
|
||||
/// return an array of edgee indices in _MTEdgeVertexIndices if the pixel at coordinate pc corresponds to the bounding box.
|
||||
function _bbox_sides(pc, pixsize, bbox) = let(
|
||||
@@ -1100,7 +1100,7 @@ function _contour_pixels(pixsize, bbox, fieldarray, fieldfunc, pixcenters, isova
|
||||
: 0.25*(f0 + f1 + f2 + f3)
|
||||
],
|
||||
pixcoord = [x,y],
|
||||
pixfound_isoval = (min(pf) < isovalue && isovalue < max(pf)),
|
||||
pixfound_isoval = (min(pf) <= isovalue && isovalue <= max(pf)),
|
||||
psides = _bbox_sides(pixcoord, pixsize, bbox),
|
||||
pixfound_outer = len(psides)==0 ? false
|
||||
: let(
|
||||
@@ -1288,7 +1288,7 @@ function _revsurf_basic(point, path, coef, neg, maxdist) =
|
||||
if (cross(seg[1]-seg[0], pt-seg[0]) > EPSILON) 1]
|
||||
? -1 : 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
neg * coef / (inside*dist+maxdist);
|
||||
neg * coef / (max(0,inside*dist+maxdist));
|
||||
|
||||
function _revsurf_influence(point, path, coef, exp, neg, maxdist) =
|
||||
let(
|
||||
@@ -1307,7 +1307,7 @@ function _revsurf_influence(point, path, coef, exp, neg, maxdist) =
|
||||
if (cross(seg[1]-seg[0], pt-seg[0]) > EPSILON) 1]
|
||||
? -1 : 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
neg * (coef / (inside*dist+maxdist))^exp;
|
||||
neg * (coef / (max(0,inside*dist+maxdist)))^exp;
|
||||
|
||||
function _revsurf_cutoff(point, path, coef, cutoff, neg, maxdist) =
|
||||
let(
|
||||
@@ -1325,7 +1325,7 @@ function _revsurf_cutoff(point, path, coef, cutoff, neg, maxdist) =
|
||||
inside = [] == [for(seg=segs)
|
||||
if (cross(seg[1]-seg[0], pt-seg[0]) > EPSILON) 1]
|
||||
? -1 : 1,
|
||||
d=inside*dist+maxdist
|
||||
d=max(0,inside*dist+maxdist)
|
||||
)
|
||||
neg * mb_cutoff(d, cutoff) * coef/d;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1345,7 +1345,7 @@ function _revsurf_full(point, path, coef, cutoff, exp, neg, maxdist) =
|
||||
inside = [] == [for(seg=segs)
|
||||
if (cross(seg[1]-seg[0], pt-seg[0]) > EPSILON) 1]
|
||||
? -1 : 1,
|
||||
d=inside*dist+maxdist
|
||||
d=max(0,inside*dist+maxdist)
|
||||
)
|
||||
neg * mb_cutoff(d, cutoff) * (coef/d)^exp;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1643,6 +1643,18 @@ function debug_tetra(r) = let(size=r/norm([1,1,1])) [
|
||||
[[0,1,3],[0,3,2],[1,2,3],[1,0,2]]
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
// Section: Metaballs (3D and 2D)
|
||||
// 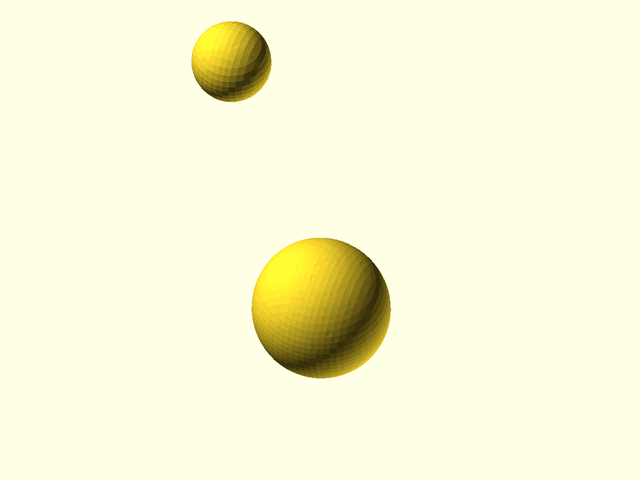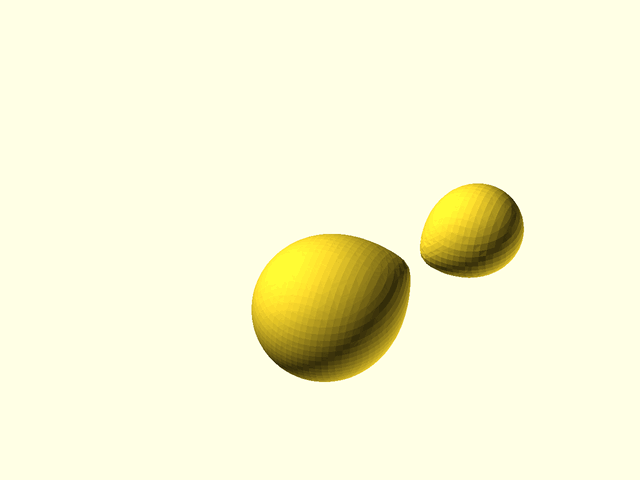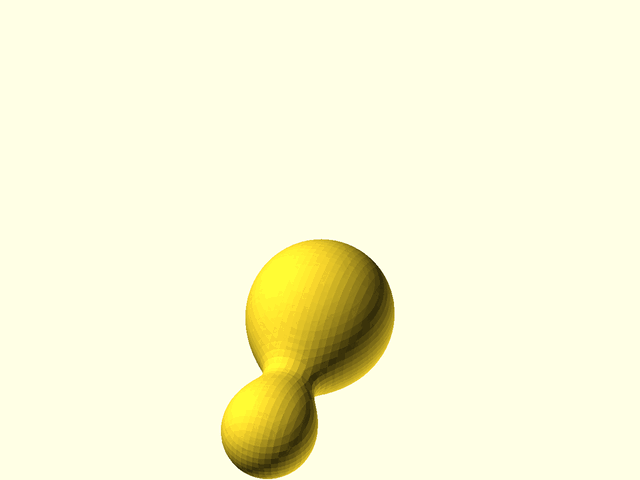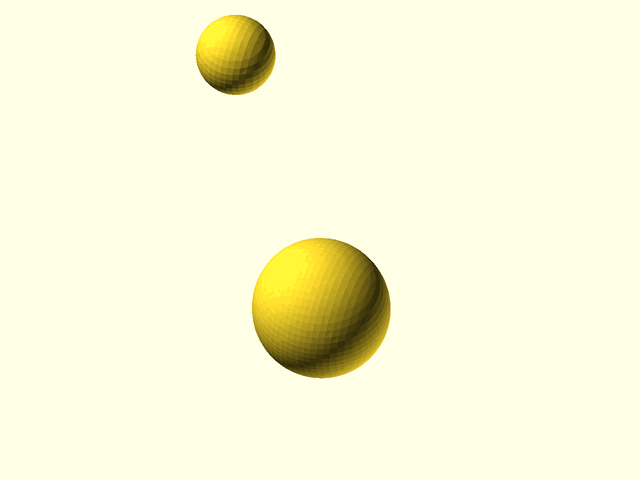
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// [Metaballs](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metaballs), also known as "blobby objects",
|
||||
// can produce smoothly varying blobs and organic forms. You create metaballs by placing metaball
|
||||
// objects at different locations. These objects have a basic size and shape when placed in
|
||||
// isolation, but if another metaball object is nearby, the two objects interact, growing larger
|
||||
// and melding together. The closer the objects are, the more they blend and meld.
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// The `metaballs()` module and function produces scenes of 3D metaballs. The `metaballs2d()` module and
|
||||
// function produces scenes of 2D metaballs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Function&Module: metaballs()
|
||||
// Synopsis: Creates a group of 3D metaballs (smoothly connected blobs).
|
||||
@@ -1654,14 +1666,6 @@ function debug_tetra(r) = let(size=r/norm([1,1,1])) [
|
||||
// Usage: As a function
|
||||
// vnf = metaballs(spec, bounding_box, voxel_size, [isovalue=], [closed=], [exact_bounds=], [convexity=], [show_stats=]);
|
||||
// Description:
|
||||
// 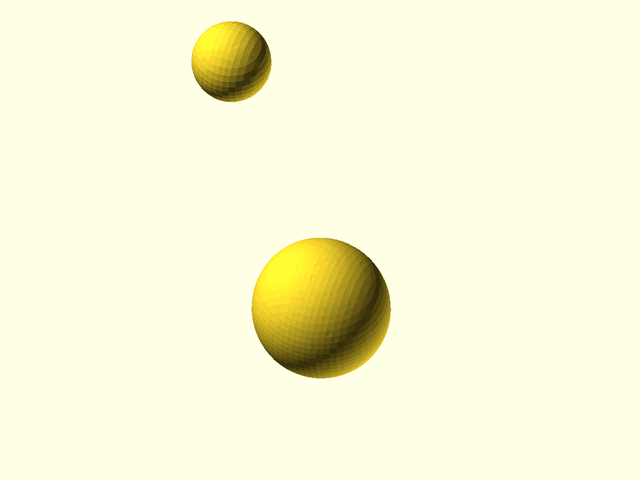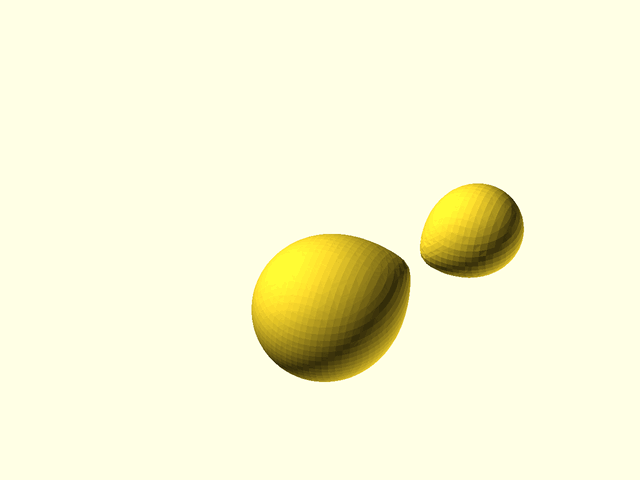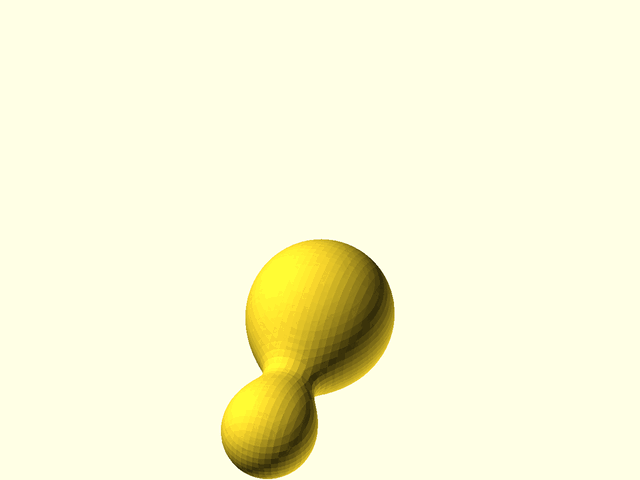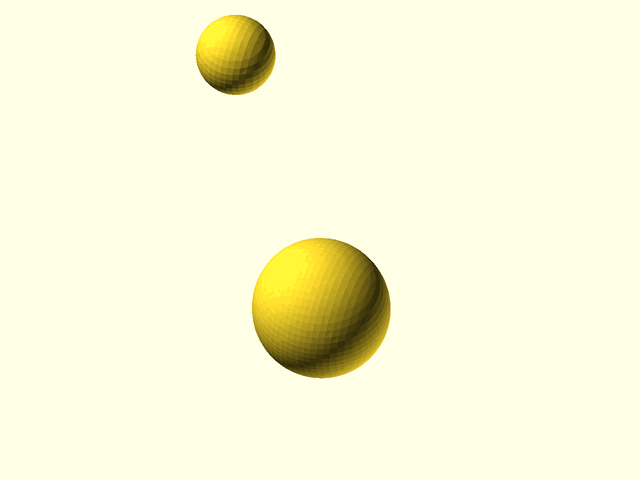
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// [Metaballs](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metaballs), also known as "blobby objects",
|
||||
// can produce smoothly varying blobs and organic forms. You create metaballs by placing metaball
|
||||
// objects at different locations. These objects have a basic size and shape when placed in
|
||||
// isolation, but if another metaball object is nearby, the two objects interact, growing larger
|
||||
// and melding together. The closer the objects are, the more they blend and meld.
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// The simplest metaball specification is a 1D list of alternating transformation matrices and
|
||||
// metaball functions: `[trans0, func0, trans1, func1, ... ]`, passed as the `spec` parameter.
|
||||
// Each transformation matrix you supply can be constructed using the usual transformation commands
|
||||
@@ -2526,7 +2530,7 @@ function mb_rect(size, squareness=0.5, cutoff=INF, influence=1, negative=false,
|
||||
|
||||
function _trapsurf_full(point, path, coef, cutoff, exp, neg, maxdist) =
|
||||
let(
|
||||
pt = [norm([point.x,0]), point.y],
|
||||
pt = [abs(point.x), point.y],
|
||||
segs = pair(path),
|
||||
dist = min([for(seg=segs)
|
||||
let(
|
||||
@@ -2540,7 +2544,7 @@ function _trapsurf_full(point, path, coef, cutoff, exp, neg, maxdist) =
|
||||
inside = [] == [for(seg=segs)
|
||||
if (cross(seg[1]-seg[0], pt-seg[0]) > EPSILON) 1]
|
||||
? -1 : 1,
|
||||
d=inside*dist+maxdist
|
||||
d=max(0,inside*dist+maxdist)
|
||||
)
|
||||
neg * mb_cutoff(d, cutoff) * (coef/d)^exp;
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2726,7 +2730,7 @@ function mb_ring(ir,or, cutoff=INF, influence=1, negative=false, hide_debug=fals
|
||||
// 0.5 you get a $1/d^2$ falloff. Changing this exponent changes how the balls interact.
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// You can pass a custom function as a [function literal](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSCAD_User_Manual/User-Defined_Functions_and_Modules#Function_literals)
|
||||
// that takes a 3-vector as its first argument and returns a single numerical value.
|
||||
// that takes a 2-vector as its first argument and returns a single numerical value.
|
||||
// Generally, the function should return a scalar value that drops below the isovalue somewhere within your
|
||||
// bounding box. If you want your custom metaball function to behave similar to to the built-in functions,
|
||||
// the return value should fall off with distance as $1/d$.
|
||||
@@ -2740,7 +2744,7 @@ function mb_ring(ir,or, cutoff=INF, influence=1, negative=false, hide_debug=fals
|
||||
// isovalue. Setting `hide_debug=true` in individual metaball functions hides primitive shape from the debug
|
||||
// view.
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// User-defined metaball functions are displayed by default as gray triangles with a corner radius of 5,
|
||||
// User-defined metaball functions are displayed by default as gray squares with a corner radius of 5,
|
||||
// unless you also designate a polygon path for your custom function. To specify a custom polygon for a custom function
|
||||
// literal, enclose it in square brackets to make a list with the function literal as the first element, and
|
||||
// another list as the second element, for example:
|
||||
@@ -2884,7 +2888,7 @@ function mb_ring(ir,or, cutoff=INF, influence=1, negative=false, hide_debug=fals
|
||||
// ];
|
||||
// metaballs2d(spec, [[-20,-20],[20,17]], pixel_size=0.5, debug=true);
|
||||
|
||||
module metaballs2d(spec, bounding_box, pixel_size, pixel_count, isovalue=1, closed=true, px_centers=false, exact_bounds=false, convexity=6, cp="centroid", anchor=CENTER, spin=0, atype="hull", show_stats=false, show_box=false, debug=false) {
|
||||
module metaballs2d(spec, bounding_box, pixel_size, pixel_count, isovalue=1, closed=true, px_centers=false, exact_bounds=false, convexity=6, cp="centroid", anchor="origin", spin=0, atype="hull", show_stats=false, show_box=false, debug=false) {
|
||||
regionlist = metaballs2d(spec, bounding_box, pixel_size, pixel_count, isovalue, closed, px_centers, exact_bounds, show_stats, _debug=debug);
|
||||
if(debug) {
|
||||
// display debug polyhedrons
|
||||
@@ -2899,7 +2903,7 @@ module metaballs2d(spec, bounding_box, pixel_size, pixel_count, isovalue=1, clos
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else { // debug==false, just display the metaball surface
|
||||
attachable(anchor, spin, two_d=true, region=regionlist) {
|
||||
region(regionlist);
|
||||
region(regionlist, anchor=anchor, spin=spin, cp=cp, atype=atype);
|
||||
children();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -2965,6 +2969,15 @@ function metaballs2d(spec, bounding_box, pixel_size, pixel_count, isovalue=1, cl
|
||||
|
||||
/// ---------- isosurface stuff starts here ----------
|
||||
|
||||
// Section: Isosurfaces (3D) and contours (2D)
|
||||
// The isosurface of a function $f(x,y,z)$ is the set of points where $f(x,y,z)=c$ for some
|
||||
// constant isovalue $c$.
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// Any 2D cross-section of an isosurface is a contour. The contour of a function $f(x,y)$ is the set
|
||||
// of points where $f(x,y,z)=c$ for some constant isovalue $c$. Considered in the context of an elevation
|
||||
// map, the function returns an elevation associated with any $(x,y)$ point, and the isovalue $c$ is a
|
||||
// specific elevation at which to compute the contour paths.
|
||||
|
||||
// Function&Module: isosurface()
|
||||
// Synopsis: Creates a 3D isosurface (a 3D contour) from a function or array of values.
|
||||
// SynTags: Geom,VNF
|
||||
@@ -2975,8 +2988,7 @@ function metaballs2d(spec, bounding_box, pixel_size, pixel_count, isovalue=1, cl
|
||||
// vnf = isosurface(f, isovalue, bounding_box, voxel_size, [voxel_count=], [reverse=], [closed=], [exact_bounds=], [show_stats=]);
|
||||
// Description:
|
||||
// Computes a [VNF structure](vnf.scad) of an object bounded by an isosurface or a range between two isosurfaces, within a specified bounding box.
|
||||
// The isosurface of a function $f(x,y,z)$ is the set of points where $f(x,y,z)=c$ for some
|
||||
// constant isovalue $c$.
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// To provide a function, you supply a [function literal](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSCAD_User_Manual/User-Defined_Functions_and_Modules#Function_literals)
|
||||
// taking an `[x,y,z]` coordinate as input to define the grid coordinate location and
|
||||
// returning a single numerical value.
|
||||
@@ -3342,10 +3354,6 @@ function _showstats_isosurface(voxsize, bbox, isoval, cubes, triangles, faces) =
|
||||
// Computes a [region](regions.scad) that contains one or more 2D contour [paths](paths.scad)
|
||||
// within a bounding box at a single isovalue.
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// The contour of a function $f(x,y)$ is the set of points where $f(x,y,z)=c$ for some
|
||||
// constant isovalue $c$. Considered in the context of an elevation map, the function returns an
|
||||
// elevation associated with any $(x,y)$ point, and the isovalue $c$ is a specific elevation at
|
||||
// which to compute the contour paths.
|
||||
// To provide a function, you supply a [function literal](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/OpenSCAD_User_Manual/User-Defined_Functions_and_Modules#Function_literals)
|
||||
// taking two parameters as input to define the grid coordinate location (e.g. `x,y`) and
|
||||
// returning a single numerical value.
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user