mirror of
https://github.com/JustinSDK/dotSCAD.git
synced 2025-01-18 06:38:14 +01:00
1.6 KiB
1.6 KiB
crystal_ball
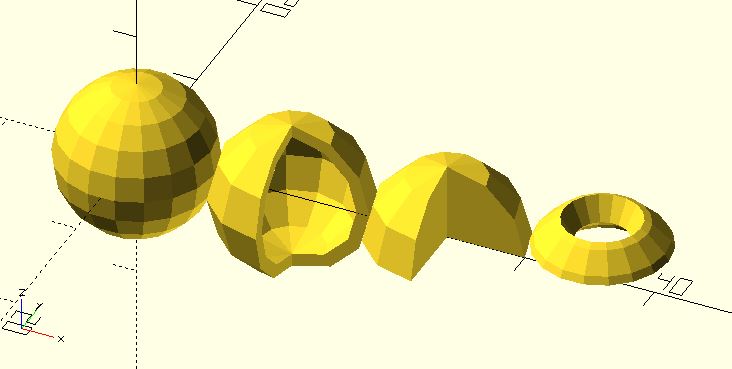
Uses spherical coordinate system to create a crystal ball.
Parameters
radius: The radial distance r.theta: The azimuthal angle. It defaults to 360. It also accepts a 2 element vector. The first element of the vector is the beginning angle in degrees, and the second element is the ending angle.phi: The polar angle. It defaults to 180. It also accepts a 2 element vector. The first element of the vector is the beginning angle in degrees, and the second element is the ending angle.thickness: The thickness of the ball. Since: 2.1.$fa,$fs,$fn: Check the circle module or the sphere module for more details. The final fragments will be a multiple of 4 to fit edges.
Examples
include <rotate_p.scad>;
include <cross_sections.scad>;
include <polysections.scad>;
include <ring_extrude.scad>;
include <crystal_ball.scad>;
crystal_ball(radius = 6);
translate([12, 0, 0])
crystal_ball(
radius = 6,
theta = 270,
thickness = 1,
$fn = 12
);
translate([24, 0, 0])
crystal_ball(
radius = 6,
theta = 270,
phi = 90,
$fn = 12
);
translate([36, 0, 0])
crystal_ball(
radius = 6,
theta = [-30, 270],
phi = [30, 60],
thickness = 2
);