mirror of
https://github.com/JustinSDK/dotSCAD.git
synced 2025-01-17 14:18:13 +01:00
1.5 KiB
1.5 KiB
voronoi3d
Create a 3D version of Voronoi diagram. The initial space for each cell is calculated automatically from the given points by the following code:
xs = [for(p = points) p[0]];
ys = [for(p = points) abs(p[1])];
zs = [for(p = points) abs(p[2])];
space_size = max([(max(xs) - min(xs) / 2), (max(ys) - min(ys)) / 2, (max(zs) - min(zs)) / 2]);
// cube([space_size, space_size * 2, space_size * 2]);
The preview or rendering of 3D Voronoi is slow. If you want to use this module, render and export the 3D Voronoi model first. Then, import the model to do what you want.
Since: 1.3.
Parameters
points: Points for each cell.spacing: Distance between cells. Default to 1.
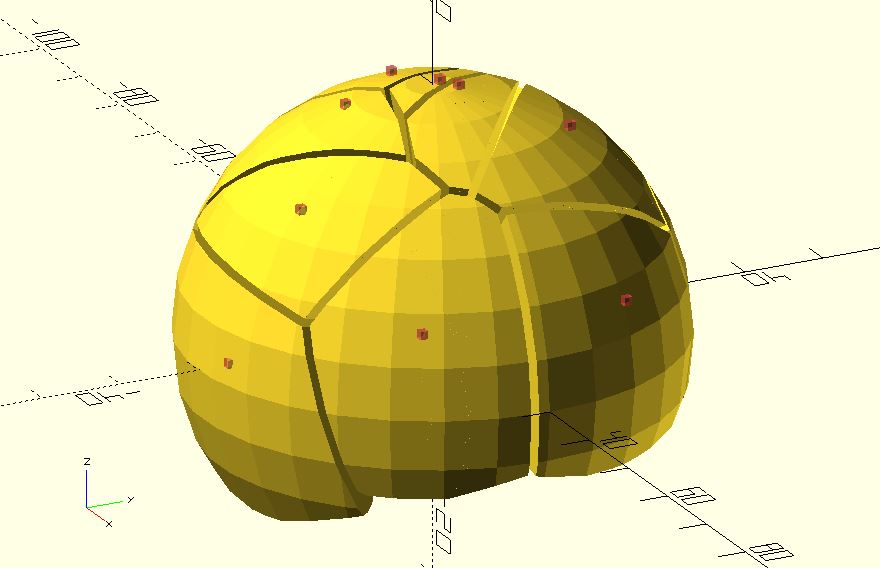
Examples
use <voronoi3d.scad>;
r = 30;
zas = rands(0, 359, 12);
yas = rands(0, 179, 12);
points = [
for(i = [0:len(zas) - 1])
[
r * cos(yas[i]) * cos(zas[i]),
r * cos(yas[i]) * sin(zas[i]),
r * sin(yas[i])
]
];
#for(pt = points) {
translate(pt) cube(1);
}
intersection() {
sphere(r);
voronoi3d(points);
}
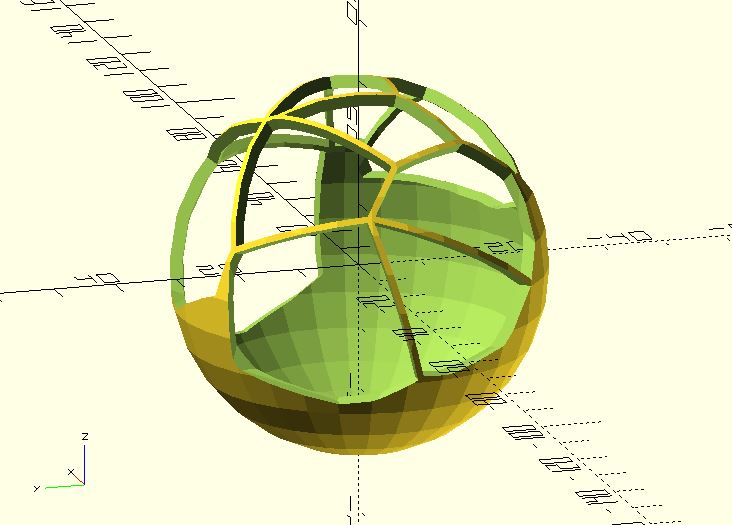
If you render, export and save the previous model as voronoi3d.stl, the following code will generate a Voronoi sphere.
r = 30;
thickness = 2;
difference() {
sphere(r);
scale(1.01) import("voronoi3d.stl");
sphere(r - thickness);
}