mirror of
https://github.com/JustinSDK/dotSCAD.git
synced 2025-01-17 22:28:16 +01:00
3.2 KiB
3.2 KiB
path_scaling_sections
Given an edge path with the first point at the outline of a shape. This function uses the path to calculate scaling factors and returns all scaled sections in the reversed order of the edge path. Combined with the sweep module, you can create an extrusion with the path as an edge.
In order to control scaling factors easily, I suggest using [x, 0, 0] as the first point and keeping y = 0 while building the edge path.
You can use any point as the first point of the edge path. Just remember that your edge path radiates from the origin.
Since: 1.2.
Parameters
shape_pts: A list of points represent a shape.edge_path: A list of points represent the edge path.
Examples
use <polyline_join.scad>;
use <shape_taiwan.scad>;
use <path_scaling_sections.scad>;
use <sweep.scad>;
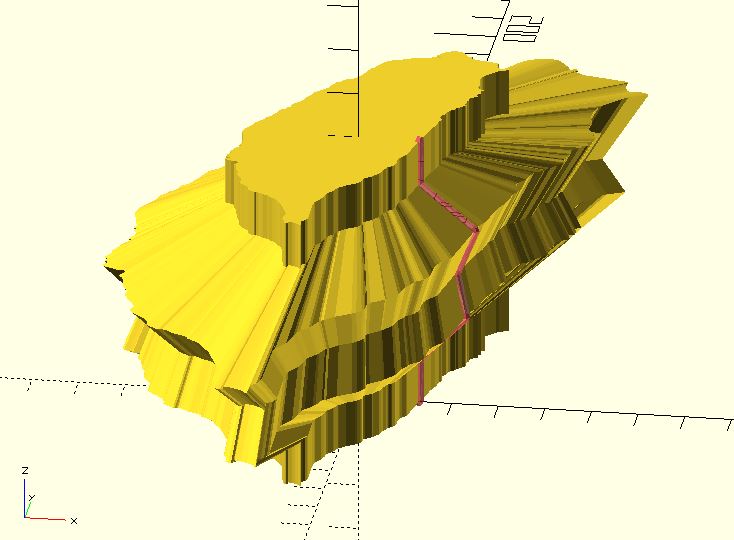
taiwan = shape_taiwan(100);
fst_pt = [13, 0, 0];
edge_path = [
fst_pt,
fst_pt + [0, 0, 10],
fst_pt + [10, 0, 20],
fst_pt + [8, 0, 30],
fst_pt + [12, 0, 40],
fst_pt + [0, 0, 50],
fst_pt + [0, 0, 60]
];
#polyline_join(edge_path)
sphere(.5);
sweep(path_scaling_sections(taiwan, edge_path));
use <polyline_join.scad>;
use <shape_taiwan.scad>;
use <path_scaling_sections.scad>;
use <sweep.scad>;
use <bezier_curve.scad>;
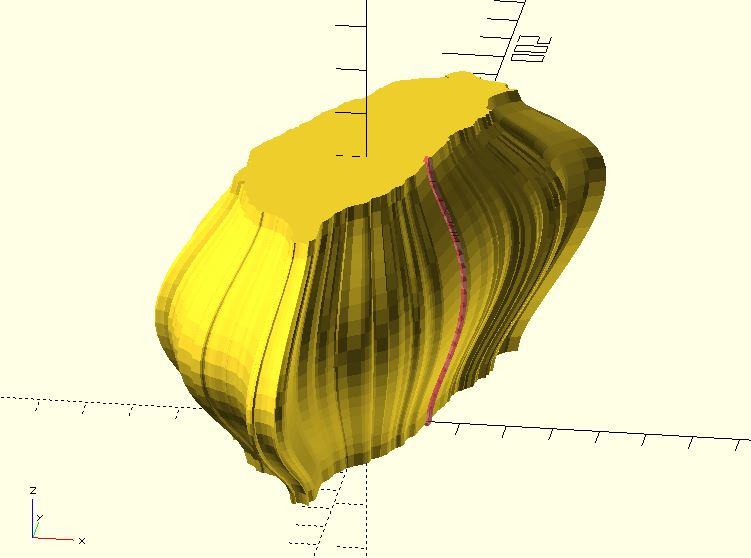
taiwan = shape_taiwan(100);
fst_pt = [13, 0, 0];
edge_path = bezier_curve(0.05, [
fst_pt,
fst_pt + [0, 0, 10],
fst_pt + [10, 0, 20],
fst_pt + [8, 0, 30],
fst_pt + [12, 0, 40],
fst_pt + [0, 0, 50],
fst_pt + [0, 0, 60]
]);
#polyline_join(edge_path)
sphere(.5);
sweep(path_scaling_sections(taiwan, edge_path));
use <shape_taiwan.scad>;
use <path_scaling_sections.scad>;
use <sweep.scad>;
use <bezier_curve.scad>;
use <ptf/ptf_rotate.scad>;
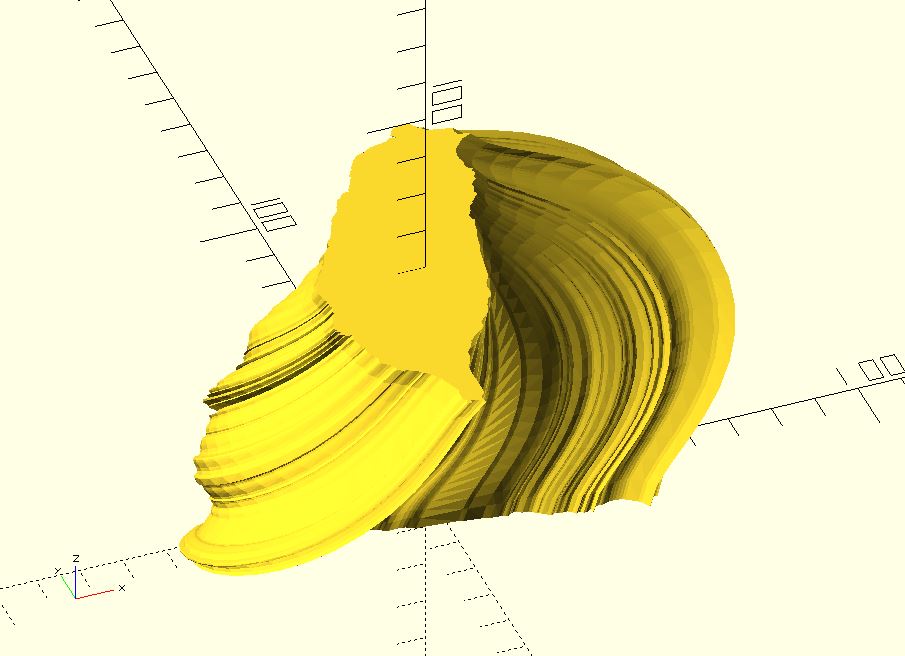
taiwan = shape_taiwan(100);
fst_pt = [13, 0, 0];
edge_path = bezier_curve(0.05, [
fst_pt,
fst_pt + [0, 0, 10],
fst_pt + [10, 0, 20],
fst_pt + [8, 0, 30],
fst_pt + [12, 0, 40],
fst_pt + [0, 0, 50],
fst_pt + [0, 0, 60]
]);
leng = len(edge_path);
twist = -90;
twist_step = twist / leng;
sections = path_scaling_sections(taiwan, edge_path);
rotated_sections = [
for(i = [0:leng - 1])
[
for(p = sections[i])
ptf_rotate(p, twist_step * i)
]
];
sweep(rotated_sections);
use <polyline_join.scad>;
use <shape_taiwan.scad>;
use <path_scaling_sections.scad>;
use <sweep.scad>;
use <ptf/ptf_rotate.scad>;
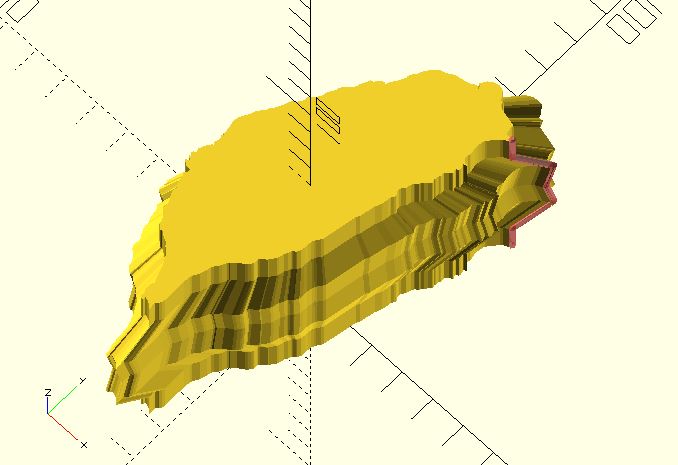
taiwan = shape_taiwan(100);
/*
You can use any point as the first point of the edge path.
Just remember that your edge path radiates from the origin.
*/
fst_pt = [taiwan[0][0], taiwan[0][1], 0];//[13, 0, 0];
a = atan2(fst_pt[1], fst_pt[0]);
edge_path = [
fst_pt,
fst_pt + ptf_rotate([0, 0, 10], a),
fst_pt + ptf_rotate([10, 0, 20], a),
fst_pt + ptf_rotate([8, 0, 30], a),
fst_pt + ptf_rotate([10, 0, 40], a),
fst_pt + ptf_rotate([0, 0, 50], a),
fst_pt + ptf_rotate([0, 0, 60], a)
];
#polyline_join(edge_path)
sphere(.5);
sweep(path_scaling_sections(taiwan, edge_path));